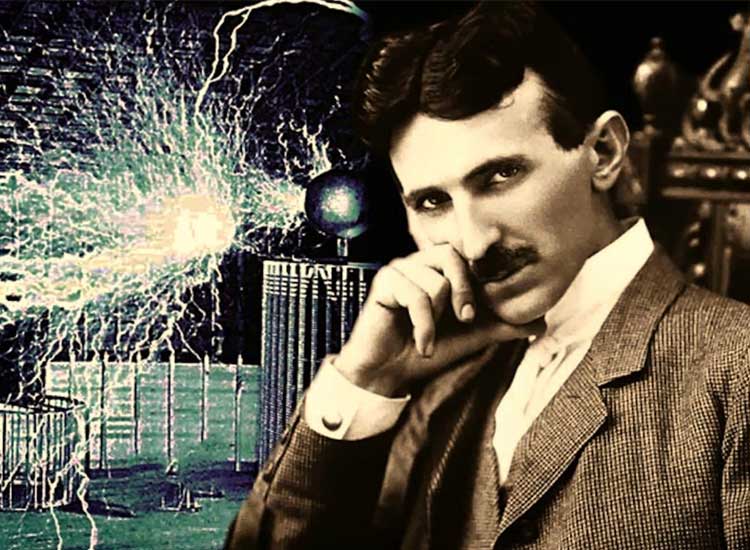
Nikola Tesla: Visoner Inventor and Pioneer of Electricity – Nikola Tesla, born on July 10, 1856 in Croatia, was a visionary inventor and one of the most influential figures in the history of electrical engineering. His contributions to the development of alternating current (AC) electrical systems, electromagnetism, and various other discoveries have left an indelible mark on the world.
Early Life and Education:
Tesla’s journey into the world of science and discovery began with his education in engineering and physics. After studying at the Technical University of Graz and the University of Prague, Tesla worked for various electrical engineering companies in Europe before moving to the United States in 1884.
Alternating Electric Current and Current Wars:
Tesla’s greatest contribution to the field of electricity was the development of alternating current (AC) power transmission. At that time, Thomas Edison was promoting direct current (DC) systems, and a fierce competition known as the “Current War” occurred. Tesla’s AC system, advocated by George Westinghouse, ultimately won out because of its efficiency in transmitting power over long distances.
Inventions and Patents:
Tesla had many patents, showing the wide range of his inventions. Among his notable contributions are the induction motor, the Tesla coil, the transformer, and the development of the Tesla turbine. His discoveries laid the foundation for modern power generation, transmission, and wireless communications technology.
Wireless Energy Transmission:
Tesla was fascinated by the idea of wireless communications and energy transmission. He envisioned a world where power could be transmitted without the need for long cables. Although his ambitious project, the Wardenclyffe Tower, intended for wireless transmission of electricity, was never completed, the concept inspired future developments in wireless technology.
Unconventional Ideas and Contributions:
Tesla’s mind was full of unconventional and futuristic ideas. He proposed the concept of free energy, worldwide wireless communications, and even implied the possibility of exploiting Earth resonances to transmit power globally. Although some of his ideas were considered ahead of their time and faced skepticism, they continue to inspire scientists and engineers to this day.
Challenges and Legacy:
Despite his intelligence, Tesla faced financial challenges throughout his life. Its focus on innovation often trumped commercial considerations, resulting in periods of financial difficulty. At the end of his life, he lived in relative emptiness and died on January 7, 1943, in New York City.
However, Tesla’s legacy endured long after his death. His discoveries and ideas paved the way for the modern electrical industry, and his name remains a symbol of innovation and ingenuity. The unit of magnetic flux, the tesla, is named in his honor, emphasizing the impact of his contributions to science and technology.
In conclusion, Nikola Tesla was a true pioneer whose revolutionary ideas and discoveries shaped the direction of electrical engineering. His legacy continues to influence generations of scientists, engineers, and inventors, reminding us of the power of imagination and the pursuit of knowledge in driving human progress.
Link Terkait :