Who is the Inventor of Electricity? These are the Figures and Their Inventions – Jakarta, Indonesia — The electricity that humans enjoy today did not just appear. There were great contributions from scientists who succeeded in discovering electricity . So, do you know who the great inventor of electricity is?
In everyday life, there is no device that does not require electricity. Namely lights, televisions, mobile phones, laptops, rice cookers, ovens, electric bicycles, electric motorcycles, electric cars, and many more.
The existence of electricity was unknown in the pre-Christian era. However, one of the Ancient Greek mathematicians discovered the theory of static electric current.
Then the theories were developed by other scientists. From theory to discovery and finally can be enjoyed by the wider community until now.
Electricity Inventor Figures
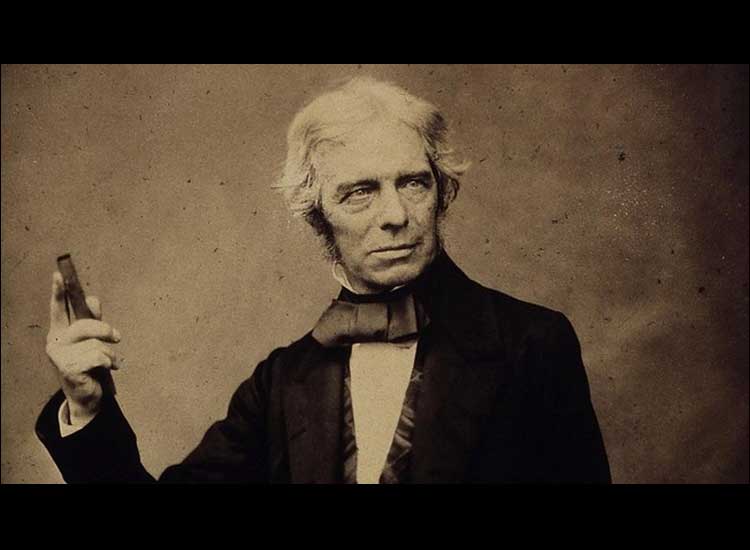
Who invented electricity? The answer is Michael Faraday who is also known as the Father of World Electricity, quoted from the e-Module of Figures and Inventions of Elementary School/Islamic Elementary School Student Book for Grade VI.
Faraday was born in 1791 in Newington, England. He came from a poor family and had little schooling.
Even so, Faraday, who was interested in the field of electricity, continued his hard work and made a major contribution through his theories and discoveries.
Quoting the book Faraday and Electricity by Neny Anggraeni, Faraday’s famous discovery is his theory of electrochemistry and electromagnetics. He observed that a copper coil connected to a battery causes a magnetic field.
In addition, he also invented a tool that later became the Bunsen burner which is used in almost all science laboratories as a practical heat source.
With the guidance of Sir Humphry Davy, a chemist who often lectured at the Royal Institution, Faraday made his discovery. Then in 1821, Faraday created the first dynamo and electric motor.
Other Figures in the History of the Discovery of Electricity
In addition to Faraday, there are a number of figures or names who have contributed to the discovery and development of electricity in the world. Who are they?
1. Thales
Thales was an Ancient Greek mathematician around 625-547 BC. Although at that time his discovery did not seem modern and sophisticated, Thales produced a simple discovery related to electricity.
Initially, Thales discovered a piece of amber that when rubbed on wool cloth, when brought close to chicken feathers, the feathers would be attracted to and stick to the amber.
Thales thought that amber had this power. At that time, Thales did not know about electricity.
Thales made several observations on static electricity which he believed caused by friction which made amber magnetic as opposed to minerals like magnets which did not require rubbing, citing the Basic Textbook of Electrical Engineering by Dr Hantje Ponto.
At that time, Thales did not know that attraction was caused by magnetic effects until science finally proved that there was a relationship between magnetism and electricity.
2. Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin had done extensive research on electricity in the 18th century which was documented by Joseph Priestley (1767) History and Present Status of Electricity.
Franklin, an American thinker and researcher, experimented by tying a metal key to a kite string during a lightning storm.
The flash that jumped from the key to his hand showed that lightning was electrical in nature. He concluded that electric current was the same as lightning.
3. William Gilbert
English scientist William Gilbert made a special study of electricity and magnetism, distinguishing the lodestone effect from static electricity produced by rubbing amber.
He proposed a new Latin word, electricus, meaning electron, to refer to the property of attracting light objects after being rubbed.
The word was eventually absorbed into English, namely electric and electricity, which first appeared in Thomas Browne’s printed work, Pseudodoxia Epidemica in 1646.
Thus information about electricity from who discovered electricity until finally developed by a number of other scientists. Hopefully useful!